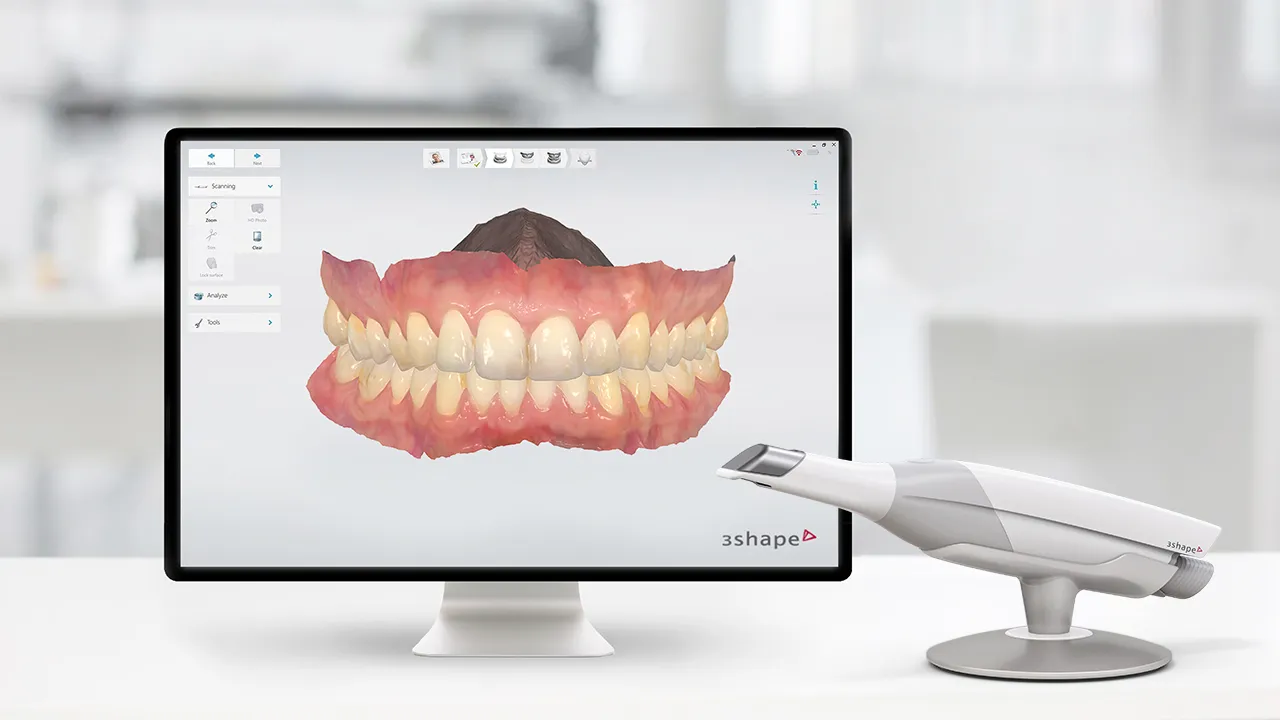
A dental optical impression, also known as a digital impression, is a method of capturing a 3D image of a tooth or dental arch using an intraoral scanner.
This technique replaces the traditional method of dental impression, which involves using a paste or moulding material to make an impression of the tooth or set of teeth.
The intraoral scanner uses an optical camera to capture high resolution images of the teeth and gums from different angles. These images are then used to create a 3D digital model of the tooth or dental arch.
The digital model can then be used to design customised dental restorations, such as crowns, bridges and dental implants, or to make orthodontic appliances such as clear aligners.
Dental optical impressions are often preferred to the traditional dental impression method because of their accuracy and speed. It also eliminates the need for potentially unpleasant casting materials for patients and reduces the risk of human error during impression taking.