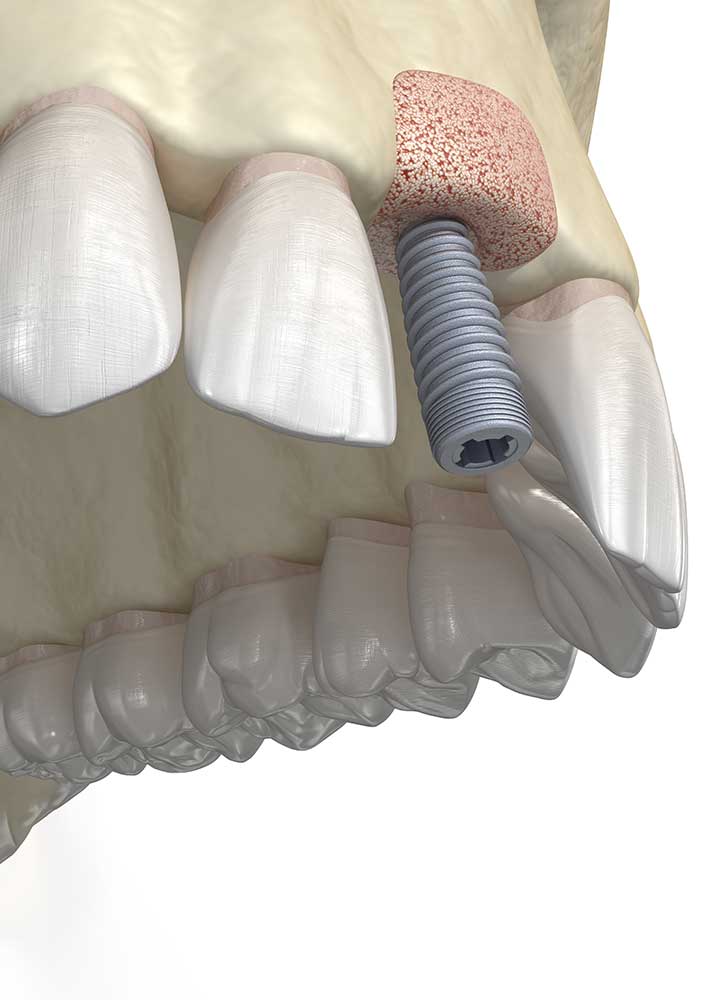
What is alveolar enhancement?
Alveolar enhancement (or alveolar filling) is a pre-implant surgery technique that minimizes bone resorption secondary to dental extractions by placing a biomaterial combined with a PRF membrane immediately after a dental extraction.
Post-extraction bone resorption is a progressive and irreversible process well described in the scientific literature.
Physiological resorption of the alveolar bone can reach up to 40% in height and 60% in width.
Insufficient bone can compromise the placement of a dental implant, sometimes necessitating the use of bone augmentation techniques.
Adequate preservation of the alveolar ridge is essential for an esthetic result and correct implant placement and therefore the use of alveolar preservation techniques can be of great interest in such cases.
The surgical procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
Pre-operative examinations are essential: intra-oral or panoramic radiography and sometimes a conebeam CT.
Tooth extraction is performed in the less traumatic way possible. In some cases, piezosurgery is indicated in order to reduce the extraction trauma and the postoperative inflammatory reaction.
The socket is then filled with bone substitute and covered with PRF membranes that will protect the biomaterial, promote the sealing of the socket, the healing of the mucosa and bone regeneration.
The wound is then closed as tightly as possible.
What are the post-surgery effects?
Following the operation, the patient may experience localized swelling in the area of the operation and in some cases a hematoma.
Post-surgery care includes:
The post-surgery period includes :