Genioplasty
What is a genioplasty?
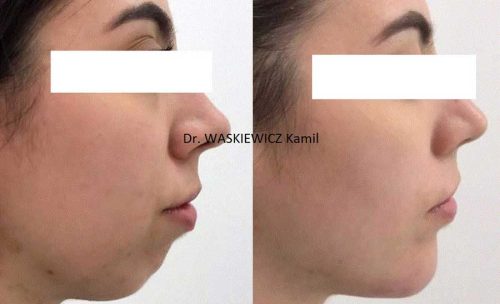
Genioplasty is a surgical procedure to alter the appearance of the chin.
The correction of an unsightly or unattractive chin helps to restore the balance of the profile and the harmony of the face.
Genioplasty has both aesthetic and functional indications.
Genioplasties are often a complement to surgical procedures on the jaws (Lefort I osteotomies, Dalpont-Obwegeser osteotomies) to increase the results and the change in profile.
What aesthetic defects can be corrected by genioplasty?
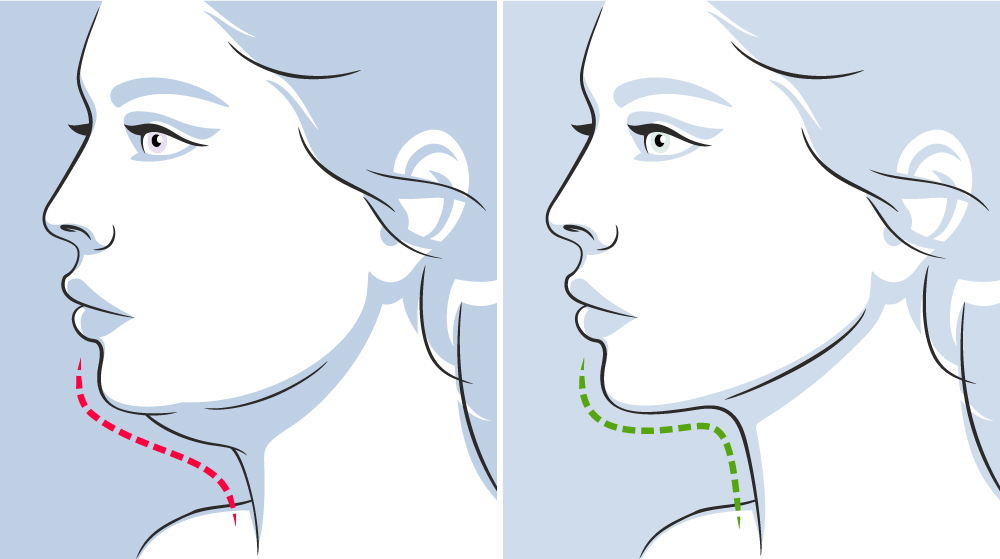
– A chin described as “receding” which is clinically characterised by a chin that is too far back.
– A chin described as “protruding” which is clinically characterised by a chin that is too far forward.
Muscles attached to the bony segments of the mandible will be displaced when the bony fragment of the chin is moved, resulting in a displacement of the soft tissues associated with the lower third of the face. and lower lips.
This may also affect the position of the lower lip. In an advanced genioplasty, the displacement of the lower lip will allow for better “lip competence” (keeping the lips in contact at rest).
A genioplasty does not affect the position of the teeth. Indeed, genioplasty is performed at a distance from the dental roots.
Nevertheless, genioplasty is frequently associated with other jaw repositioning surgeries (Lefort I, Dalpont-Obwegeser).
In cases of mandibular retrognathia (mandible too far back), surgical repositioning of the mandible by a Dalpont-Obwegeser osteotomy will then be chosen allowing in certain cases a correct repositioning of the chin and thus avoiding a genioplasty.
The surgery is performed under general anaesthesia in a day hospital.
Pre-operative examinations are essential: panoramic X-ray, profile teleradiography and conebeam CT as well as a pre-operative consultation with the anaesthetist.
The incision is made in the mouth. It concerns the gum below the lower incisors. It is therefore invisible; there is no incision in the skin.
Then the osteotomy itself is carried out, which allows the chin to be separated from the mandibular body. This is done with the help of piezosurgery, which has the advantage of making a clean cut, being less traumatic for the soft tissues and reducing post-operative inflammation and oedema.
The part that has just been separated can then be mobilised in order to reposition it in its ideal position.
This ideal position is determined by various elements
the pre-operative radiological assessment (teleradiography of the skull in profile).
the surgical guide made by 3D printing thanks to the preoperative CT conebeam.
The rest of the operation consists of reattaching the chin to the rest of the mandible in its new position. This is the osteosynthesis, which is carried out using mini-plates and titanium screws.
The operation ends with the closure of the oral incision with absorbable thread.
The duration of the operation varies according to the technical difficulties. It lasts on average 45 minutes when the genioplasty is not associated with an osteotomy of the mandible or maxilla.
Post-operative care includes:
– Mouthwash.
– Pain medication (analgesics).
– Medication for swelling (anti-inflammatories).
– Antibiotics are given during the operation and are extended in some cases.
– Ice is applied to the mouth for the first 24 hours (ice has a good anti-inflammatory and anti-edema effect).
– Food should be liquid for the first few days after the operation, then mixed or ground for the next 5 to 6 weeks.
– Brushing your teeth, even if it is difficult, must remain as careful and rigorous as possible during the post-operative period.
– It is necessary to stop smoking during the post-operative period. Continued smoking favours complications linked to poor healing of the gums.
The post-operative period includes :
– Small amounts of bleeding that may occur in the operated area during the first 24 hours.
– The pain in the operated area subsides with the prescribed analgesics and anti-inflammatories and generally disappears in a few days.
– Oedema is frequent and often marked. It is unpredictable and varies from one person to another.
Finally, the presence of plaques and screws can sometimes become annoying over time. Their removal then becomes necessary during a second operation which will never be performed before the seventh month after the first operation.
